The module whisperers
In its current issue, the trade magazine "Sonnenenergie" reports on a new method developed by HI ERN researchers to non-destructively characterize PV backsheets in the field.
For evaluations over a longer period of time, monitoring, e.g. recording of current, voltage of strings, inverters or modules, is required. An established parameter for evaluating the performance of photovoltaic power stations is the performance ratio, as the ratio of the actually generated power to the theoretically expected power. Thus, the performance ratio necessarily requires knowledge of solar insolation. However, this data is often missing from the plants or is only available to a limited extent.
Researchers at the Helmholtz Institute Erlangen-Nuremberg for Renewable Energies (HI ERN) have now developed a new approach that makes it possible to detect and quantify insufficient power independently of weather data. This newly developed self-referencing algorithm analyzes the performance of plants based on monitoring data of arbitrary time periods. The researcher:s study shows that the performance of each string in the photovoltaic system can be quantified, localized and visualized.
HI ERN researchers Dr. Claudia Buerhop-Lutz, Tobias Pickel, Dr. Jens Hauch, and Dr. Ian Marius Peters present the potential of the self-referencing algorithm (SR) in their study. For this purpose, the algorithm is compared with the established performance ratio (PR). The study was recently published in Progress in Photovoltaics and has already been picked up by pv magazine.
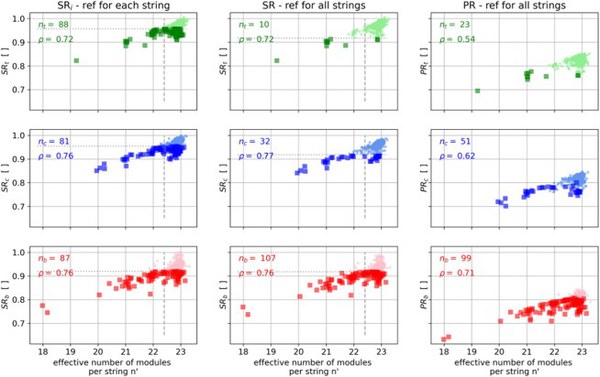
The newly developed algorithm can be used not only to inspect photovoltaic modules, but also strings, arrays, inverters and transformers. Potential is offered by the self-referencing method for degradation studies of time series and root cause analyses with machine learning and the combination with different data sources, for example image data.
Claudia Buerhop, Tobias Pickel, Jens Hauch, Ian Marius Peters
Assessment of string performance using self-referencing method in comparison to performance ratio
Prog Photovolt Res Appl. 2022; 1- 7. doi:10.1002/pip.3649
First published: 08 November 2022
Abteilungsleiter Teamleiter "High Throughput Materials and Devices"